What Is a Containerized Wastewater Treatment Plant?

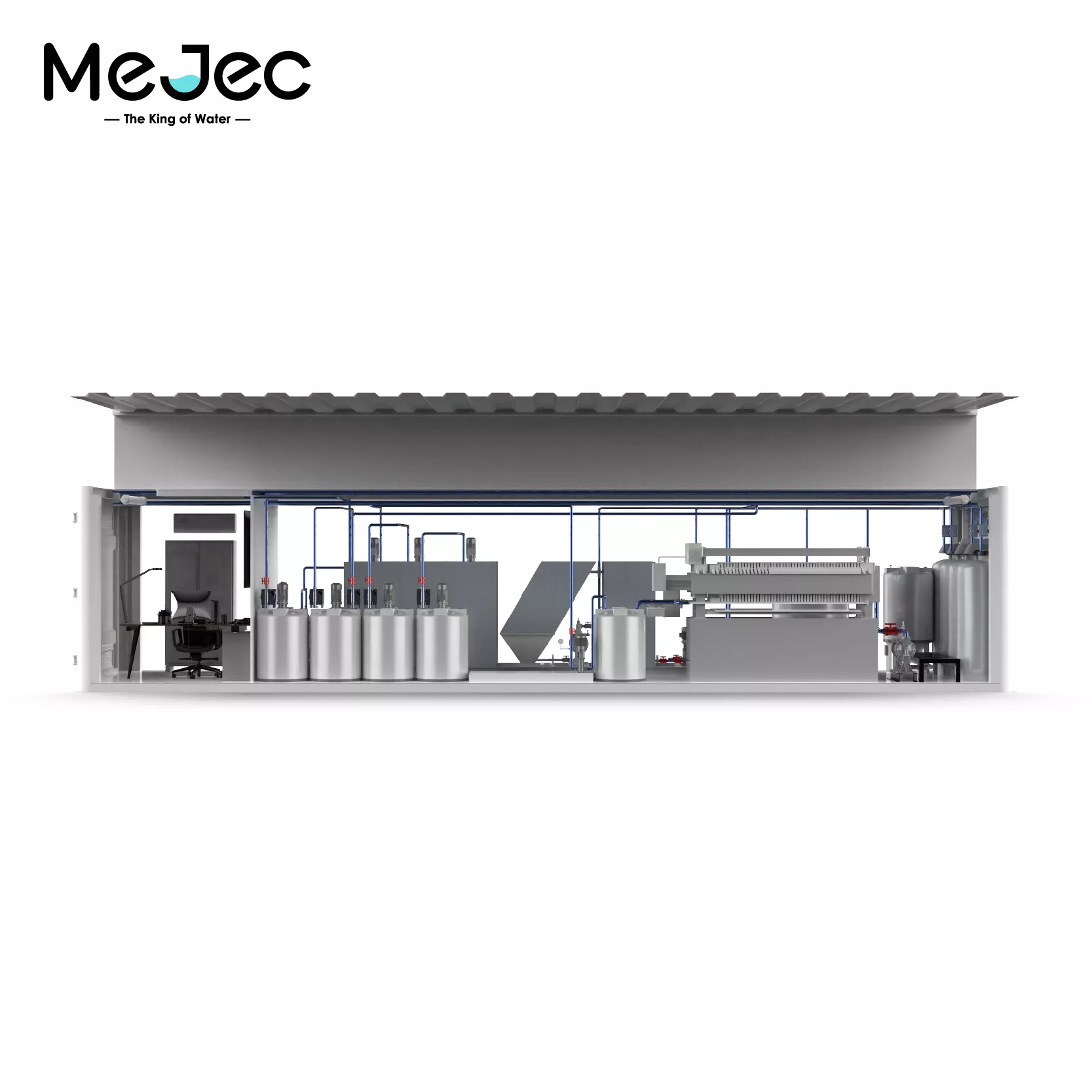
A containerized sewage treatment plant is a compact system that treats wastewater inside a standard shipping container. The design allows for fast setup and easy relocation. These plants stand out because they arrive pre-assembled and can be quickly deployed where traditional infrastructure is not available.
Feature | Containerized Plants | Traditional Plants |
|---|---|---|
Deployment Time | Quick installation and commissioning | Extensive infrastructure and civil works |
Mobility | Trailer-mounted for rapid deployment | Fixed-location, less mobile |
Ideal Use Cases | Remote locations, emergency response | Permanent installations |
Many communities and organizations choose containerized solutions for emergencies, camps, and remote sites. The global market reached $2.84 billion in 2024 and is forecasted to grow to $5.29 billion by 2033, showing strong demand for containerized sewage treatment plant options.
Key Takeaways
Containerized wastewater treatment plants are compact systems that treat sewage in standard shipping containers, allowing for quick setup and easy relocation.
These plants use advanced technologies like MABR and MBR to improve efficiency, reduce energy use, and produce high-quality effluent.
The modular design of containerized plants allows for easy expansion and adaptation to changing treatment needs, making them ideal for various applications.
Containerized systems are perfect for emergency situations, remote locations, and temporary camps, providing fast and reliable sanitation solutions.
Choosing a containerized plant can save time and costs, with minimal civil works and quick operational readiness.
Key Features of Containerized Sewage Treatment Plant
Modular Design and Integration
A containerized sewage treatment plant uses a modular approach to simplify installation and expansion. Each system is built inside a standard container, making it compact and easy to transport. The modular design allows for quick adaptation to different treatment needs and site conditions. Operators can add or remove modules to match changing requirements, such as increased wastewater volume or stricter regulations.
Feature | Description |
|---|---|
Compactness | The system fits inside a container, saving space and allowing placement in tight areas. |
Adaptability | Modules can be deployed rapidly and adjusted for various treatment goals. |
Integration | The structure supports easy expansion and customization for specific projects. |
Highly integrated modules separate key components, such as the anoxic tank and membrane tank, for efficient operation.
Transportability enables deployment in remote or temporary locations.
Cost-effective expansion lets users customize the plant to meet local standards.
The market for modular containerized sewage treatment plant solutions continues to grow. Many organizations choose these systems for their scalability and lower costs compared to traditional plants. For example, adding more pre-assembled containers increases treatment capacity without major construction.
Core Technologies (MABR, MBR, SWRO)
Modern containerized sewage treatment plants use advanced technologies to improve efficiency and output quality. The Mejec JM series features several core processes:
MABR (Membrane Aerated Biofilm Reactor): This technology supplies oxygen directly to biofilms using gas-permeable membranes. It reduces energy use by up to 75% compared to traditional aeration. MABR also supports simultaneous nitrification and denitrification, which improves nitrogen removal.
MBR (Membrane Bioreactor): MBR combines biological treatment with membrane filtration. It produces high-quality effluent and minimizes sludge production. The system uses reinforced hollow fiber membranes for durability and fouling resistance.
SWRO (Seawater Reverse Osmosis): SWRO converts seawater into freshwater using high-pressure membranes. The process includes energy recovery and anti-corrosion materials, making it suitable for harsh environments.
These technologies allow containerized sewage treatment plants to handle a wide range of wastewater types, from domestic to industrial and even seawater desalination. The systems are factory pre-assembled, which ensures consistent quality and rapid deployment.
Operation and Control Systems
Operation and control systems play a vital role in the reliability and efficiency of containerized sewage treatment plants. Most systems feature automatic operation, reducing the need for manual intervention. Intelligent control units monitor performance and adjust processes in real time.
Feature | Description |
|---|---|
Remote Access Technology | Operators can control the plant from mobile devices or computers, making adjustments as needed. |
Automatic Operation | The system runs independently, minimizing human error and labor costs. |
Intelligent Control Systems | Advanced monitoring ensures stable operation and quick response to any issues. |
Remote Monitoring | Supervisors can oversee system performance from any location, improving maintenance and reliability. |
Smart automation enables real-time monitoring and remote management.
Automatic alerts notify operators of faults, reducing downtime.
Wide-area monitoring and control functions improve overall reliability.
Plug-and-play setup and factory pre-assembly make these plants easy to install and maintain. Even staff with limited technical experience can operate the system after brief training. These features help organizations meet regulatory standards while saving time and energy.
How Containerized Wastewater Treatment Works

Treatment Process Overview
A containerized sewage treatment plant uses a step-by-step process to clean wastewater. The process starts with pretreatment. Large solids and debris are removed using screens and grit chambers. This step protects the equipment and prepares the water for further treatment.
Next, the water enters the biological or physicochemical treatment stage. In biological treatment, bacteria break down organic matter. Advanced technologies like Membrane Aerated Biofilm Reactor (MABR) and Membrane Bioreactor (MBR) help bacteria work more efficiently. These systems allow for simultaneous nitrification and denitrification, which means they remove nitrogen in one step. Physicochemical treatment uses chemicals and filters to remove heavy metals and balance pH, especially in industrial wastewater.
After biological or physicochemical treatment, the water goes through disinfection. Ultraviolet (UV) light or chlorine kills harmful bacteria and viruses. The final step is output. Clean water leaves the plant, ready for discharge or reuse.
The following table shows typical performance values for containerized systems:
Feature | Value |
|---|---|
Hydraulic Retention Time | Approximately 2 hours |
Chemical Oxygen Demand Removal | Approximately 60% |
Nitrogen Removal | Approximately 20% |
Phosphorus Removal | Approximately 30% |
Tip: The compact design of these plants means they can treat water quickly, often in just a few hours.
Energy and Resource Efficiency
Containerized wastewater treatment systems are designed for high efficiency. They use less energy and resources than many traditional plants. Advanced membrane technologies, such as MABR and MBR, reduce the need for energy-intensive aeration. The use of gas-permeable membranes in MABR can cut energy use by up to 75%.
The table below compares containerized systems with conventional systems:
Feature | Containerized Systems | Conventional Systems |
|---|---|---|
Installation Time | Pre-assembled and pre-tested, reducing on-site time | Longer installation periods |
Scalability | Easily expandable by adding units | Often requires significant redesign |
Cost-effectiveness | Lower construction and operational costs | Higher costs due to extensive labor |
Technology Integration | Advanced membrane technology for superior filtration | May use older, less efficient methods |
Performance Consistency | Controlled environment minimizes external impact | More affected by environmental factors |
Energy consumption depends on the type of water being treated. For non-potable water, energy use ranges from 1.5 to 3 kWh per cubic meter. For potable water, it ranges from 4 to 6 kWh per cubic meter.
Water Type | Energy Consumption (kWh/m³) |
|---|---|
Non-potable | 1.5 - 3 |
Potable | 4 - 6 |
Note: Pre-assembled modules and smart controls help save both time and money during installation and operation.
Compliance and Output Quality
Containerized wastewater treatment plants are built to meet strict regulatory standards. They use multiple treatment stages—primary, secondary, and advanced—to remove contaminants and produce high-quality effluent. These systems are suitable for discharge into the environment or for reuse in irrigation and industrial processes.
Typical output water qualities are shown in the table below:
Parameter | Feed Water Quality | Expected Permeate Quality |
|---|---|---|
pH | 6.5-7.5 S.U. | 6.5-7.5 S.U. |
TSS | 200 mg/L | <5 mg/L |
BOD | 250 mg/L | <10 mg/L |
COD | 400 mg/L | <50 mg/L |
Ammonium-Nitrogen | 30 mg/L | <2 mg/L |
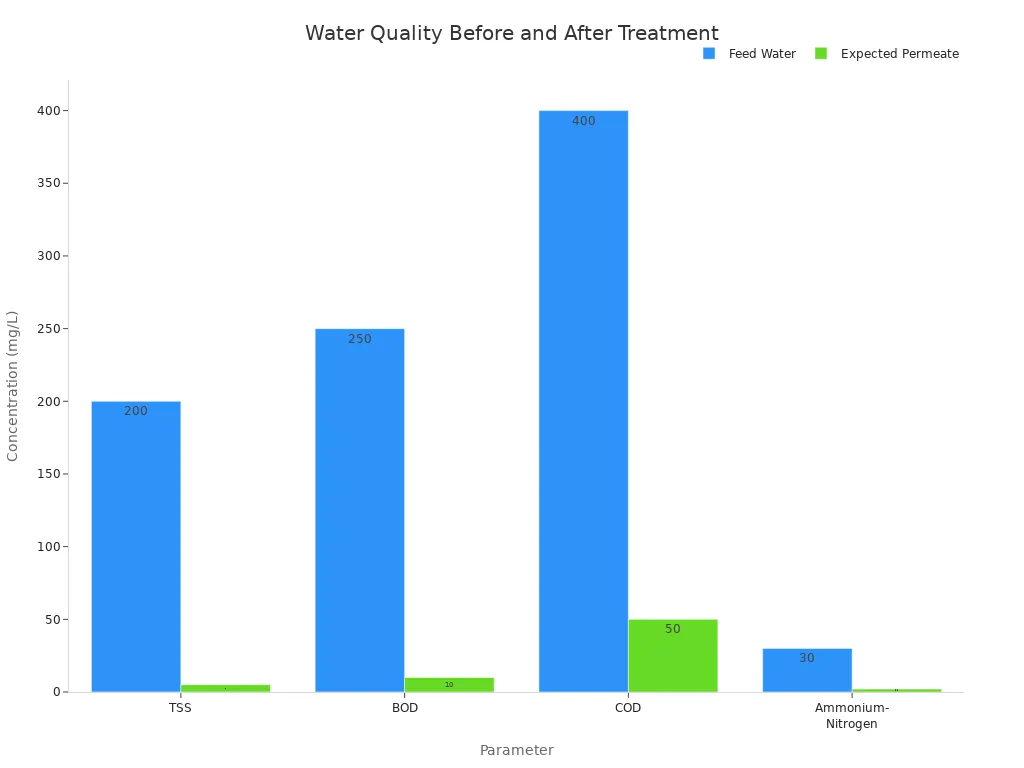
These results show that the treated water has low levels of suspended solids, organic matter, and nitrogen. The bactericidal rate can reach up to 99.9% with UV disinfection. This high level of treatment helps protect public health and the environment.
Callout: Containerized sewage treatment plant solutions provide reliable compliance with local and international water quality standards.
Application of Containerized Wastewater Treatment Plants
Emergency and Disaster Relief
Containerized wastewater treatment plants play a vital role during emergencies and natural disasters. When floods, earthquakes, or other crises damage local infrastructure, these mobile systems provide fast and reliable sanitation.
They can be set up in just a few days, much faster than traditional plants that may take months or years.
Units arrive pre-assembled and factory-tested, so only simple connections for water, electricity, and effluent are needed on-site.
Mobile water treatment units can begin producing safe water within hours of arrival.
Modular designs allow for rapid deployment, making them ideal for disaster relief and emergency response.
Note: Quick setup and easy operation help protect public health in challenging situations.
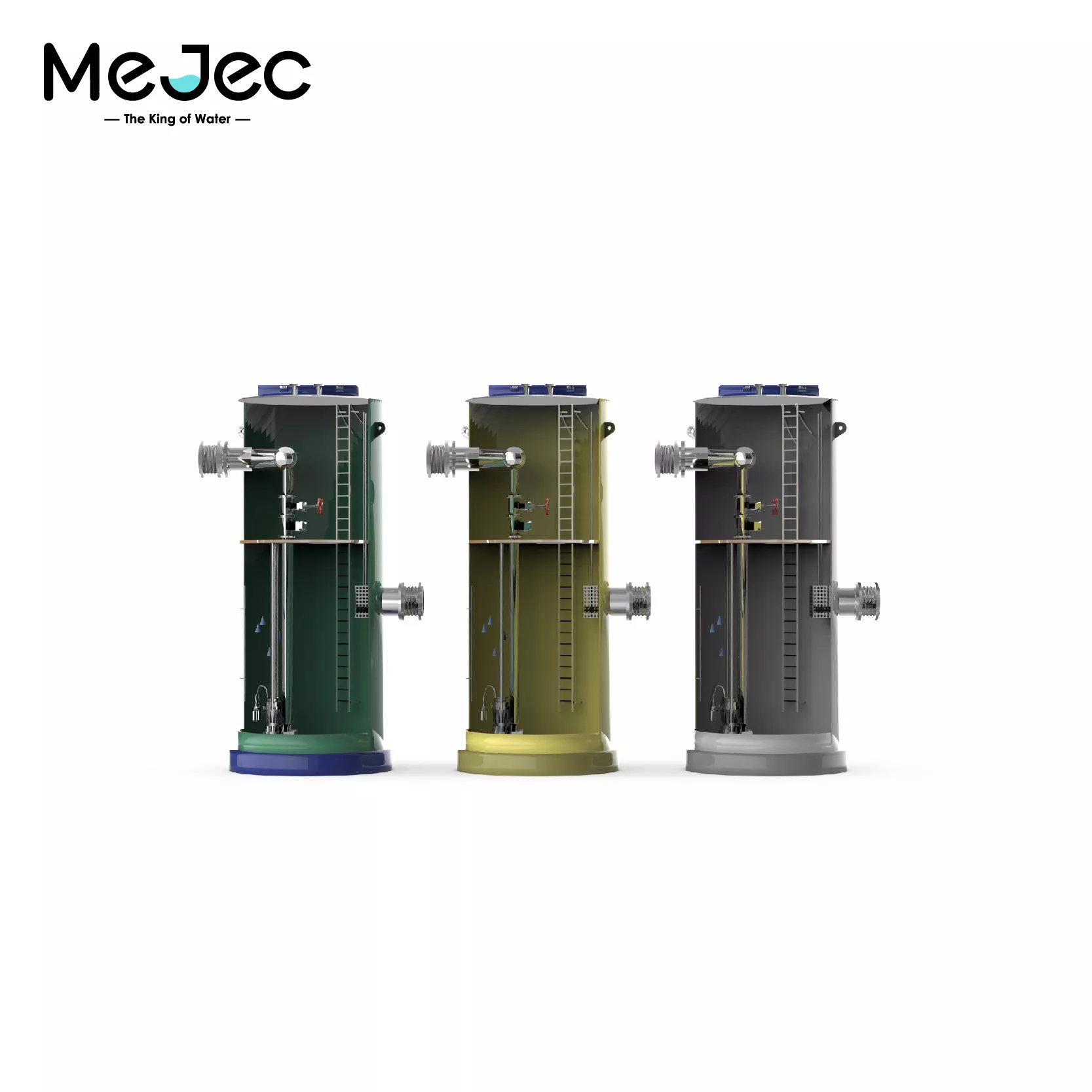
Remote and Temporary Camps
Many remote camps, such as those for refugees, military personnel, or construction workers, lack access to permanent sewage systems. A containerized sewage treatment plant offers a practical solution for these sites.
Typical capacity ranges from 50 to 2,000 m³/day, meeting the needs of both small and large camps.
The compact design allows for delivery to almost any location with only a level surface required for installation.
Challenge | Solution |
|---|---|
Adapting to the Operating Environment | Use of robust air conditioning and thermal insulation to protect equipment. |
Brine Management | Smart solutions like evaporation ponds for treating wastewater. |
Maintenance and Specialization | Specialized operator training due to compact design. |
Internet of Things (IoT) | Advanced sensors for real-time monitoring of water quality. |
Autonomous Operation | Intelligent systems that adjust parameters to maintain water quality. |
Smart controls and remote monitoring make operation simple, even in harsh climates.
Municipal, Industrial, and Tourism Uses
Containerized wastewater treatment plants serve many sectors beyond emergencies and camps.
Municipalities use them for urban wastewater management, especially during upgrades or repairs to existing systems.
Industries rely on these plants for treating specific types of wastewater, such as from mining or metal processing.
Tourism sites, including resorts and remote campsites, benefit from reliable sanitation with minimal environmental impact.
Feature | Description |
|---|---|
Portability | Easily transported and set up in various locations. |
Customization | Tailored to meet specific treatment needs for different sectors. |
Energy Efficiency | Uses less energy compared to traditional systems. |
Ease of Installation | Quick setup process, reducing downtime for operations. |
These systems help meet strict regulations, such as biological nutrient removal standards and California’s Title 22.
They provide a temporary or permanent solution while ensuring compliance with environmental laws.
Containerized sewage treatment plant solutions adapt to different climates, offer rapid setup, and support regulatory compliance across many industries.
Benefits and Considerations
Portability and Flexibility
Containerized wastewater treatment plants offer outstanding portability and flexibility.
Easy Transportation: These systems fit into standard shipping containers, making them simple to move by truck, ship, or rail.
Quick Setup: Rapid deployment means the plant can be operational within days, reducing downtime and ensuring fast access to clean water.
The modular structure allows for easy adjustments in capacity. Operators can expand or reduce the system to meet changing demands. This adaptability is important for communities with fluctuating populations. The design also supports global shipping, which increases flexibility for different environments.
Tip: Modular plants can be relocated or expanded as needs change, providing long-term value for diverse sites.
Cost and Time Savings
Containerized plants deliver significant savings in both cost and time.
Minimal civil construction reduces installation time by more than two-thirds compared to traditional plants.
Rapid delivery and easy installation allow for quick operational readiness.
Modular design enables communities to start with smaller, affordable systems and expand as needed.
Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
Reduced Installation | Less site work means faster setup and lower costs. |
Scalable Investment | Start small and add modules as demand grows. |
Lower Shipping Costs | Standard containers keep transport expenses down. |
Prefabrication and factory testing ensure reliability and minimize onsite labor. These features help organizations meet compliance deadlines and reduce overall project costs.
Factors for Selection and Deployment
Selecting and deploying a containerized plant requires careful consideration of several factors.
Factor | Description |
|---|---|
Capital Expenditures (CAPEX) | Includes civil works, process equipment, and engineering costs. |
Operational Expenditures (OPEX) | Covers energy, staffing, and maintenance. |
Flow Rate and Capacity | Impacts design and infrastructure costs. |
Quality of Source Water | Determines treatment complexity. |
Technology Choice | Affects efficiency and operational costs. |
Material of Construction | Influences durability and maintenance. |
Automation and Control Systems | Improves operational efficiency. |
Location and Accessibility | Affects transport and installation costs. |
Site requirements are minimal. Most plants need only a concrete slab, basic piping, and electricity. Maintenance is straightforward, with modular units allowing for easy upgrades or repairs. When choosing a system, consider treatment capacity, durability, and installation efficiency to ensure reliable performance.
Containerized sewage treatment plants offer a practical solution for treating wastewater in many settings. These systems stand out for their flexibility, rapid deployment, and efficiency.
Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
Flexibility | Customizable for different industries and locations |
Rapid Deployment | Operational in a short time, ideal for urgent situations |
Efficiency | High-quality treatment with lower installation costs |
Many industries, from manufacturing to disaster relief, benefit from these plants. Modular design and advanced technology help communities adapt to changing needs. Before choosing a system, review your site conditions and treatment goals.
FAQ
What is a containerized wastewater treatment plant?
A containerized wastewater treatment plant is a compact system built inside a shipping container. It treats sewage or industrial wastewater on-site. The plant arrives pre-assembled and can be quickly set up almost anywhere.
How fast can a containerized plant be installed?
Most containerized plants can be installed and started within a few days. Only basic site preparation, such as a level surface and utility connections, is needed.
Where are containerized wastewater treatment plants used?
These plants serve remote camps, disaster relief sites, construction projects, small towns, and industries. They also support seasonal tourism and emergency situations.
Tip: Containerized systems work well in places without existing sewage infrastructure.
What maintenance do these systems require?
Routine maintenance includes checking filters, cleaning membranes, and monitoring control systems. Most tasks are simple and can be done by trained local staff.
Can the treated water be reused?
Yes. Treated water often meets standards for irrigation, industrial use, or safe discharge. Some systems even produce water suitable for drinking after advanced treatment.

















.webp)


.webp)


